
PoS vs PoA vs Zero Knowledge – Their Role on The Blockchain
Bware Labs Team
Proof of stake came as the greener and more energy-efficient alternative for proof of work. On the same principle, proof of authority promised to be a better alternative to proof of stake since it requires fewer computational resources.
Unlike PoS and PoA which fall into the consensus categories, Zero Knowledge is an encryption method, but it uses an algorithm that offers users what the blockchain system promised from the beginning: ultimate privacy.
Let’s uncover how each of them works, their role on the blockchain, and their specific use cases.
General Overview of Consensus Algorithms
Blockchains need a way to keep their integrity and sustainability. That’s where consensus protocols and algorithms come into play. A consensus protocol includes a set of methods and rules implemented to ensure agreement, trust, and security occur across a decentralized network.
For instance, in the case of cryptocurrencies, a consensus mechanism helps keep track of how much currency or data each user has within a cryptocurrency’s ecosystem. Based on an algorithm, a trader isn’t allowed to spend coins more than once; otherwise, the entire system would be prone to theft.
What is Proof-of-Stake?
Proof-of-stake (PoS) is a cryptocurrency consensus mechanism used for validating and processing transactions and creating new blocks in a blockchain.
Polkadot, Avalanche, Cardano, and recently, Ethereum are a few examples of blockchain ecosystems that use PoS.
Within this consensus, each participant has to stake some of their cryptocurrency as a safety net against fraud. In return, they get the chance to become validators, which means checking new blocks of transactions; if these blocks meet protocol requirements, they will then add them to the blockchain. The more crypto you stake, the higher the chances of becoming a validator.
How PoS Works
- The proof-of-stake algorithm selects a node to be the validator of the next block; the selection process is pseudo-random; choosing validators can work as a lottery system, or based on the amount of staked tokens or the time period of staked tokens.
- Nodes on the network stake a certain amount of crypto currencies to become validators.
- Validator nodes whose “blocks” of transactions get added to the ledger receive a reward in the form of cryptocurrency.
If a trader adds a transaction to the blockchain that other validators determine is invalid, they can lose a part of the stake coins, a process called slashing.
Traders can also join staking pools, where groups of validators come together to become validators. When a staking pool is selected to receive the reward, this is split among the pool’s members, with a slightly larger share for the pool’s owner.
Benefits and Drawbacks
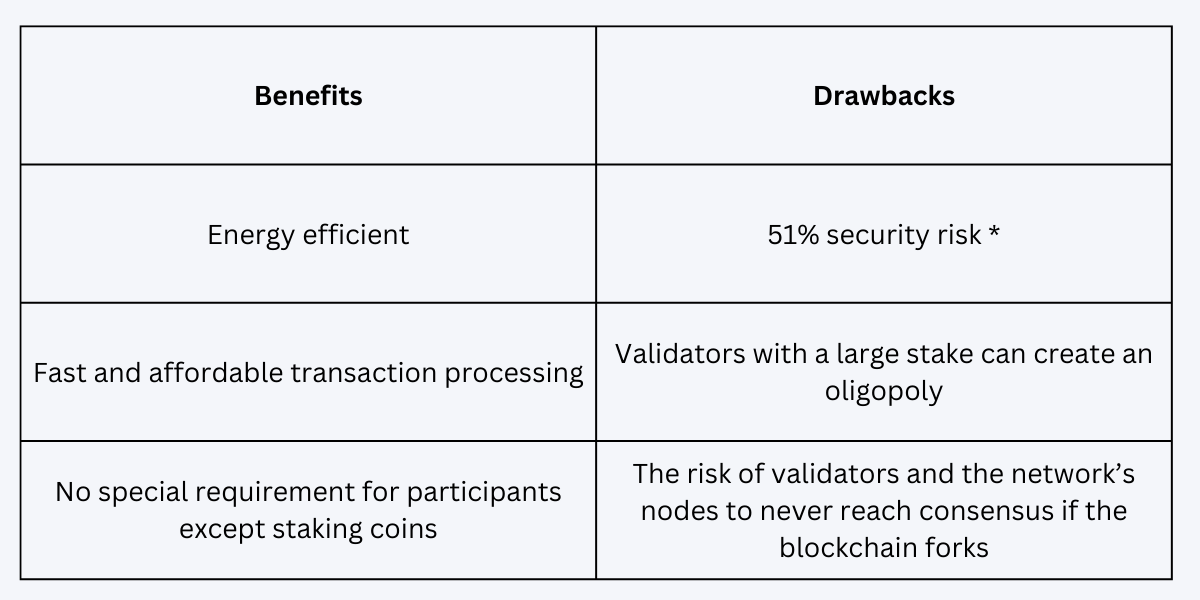
* If one participant or a group accumulates 51% or more of a currency, they’ll have 100% control of the blockchain. This is a risk since they can act in their own best interests, like reverse transactions or double-spend the native crypto token. This is known as a 51% attack.
What is Proof-of-Authority?
The Proof-Of-Authority (PoA) is a consensus method that allows only authorized and usually a small number of actors or entities to validate transactions in a blockchain network.
PoA is commonly known as the consensus algorithm that’s based on reputation since the essence of how it works is based on trust in the validator’s identity. So, instead of staking coins, validators stake their very own reputation.
All validators must meet these three requirements:
- trustworthy, with good moral standards, and without a criminal record
- their identity must be validated on the network (requires checking personal information and validators to confirm their real identities)
- willing to stake their own reputation and also invest money
The Proof of Authority model aims to help companies keep their privacy while seizing the advantages of blockchain technology.
Examples of companies that use PoA:
- Microsoft Azure – provides solutions for private networks, where clients verify transactions more efficiently without a native currency like the ether ‘gas’
- JP Morgan, with the JPMCoin – supports the audit of their funds movements for accounting purposes, with reduced costs for implementing this service.
How PoA Works
- One or more validating machines generate new blocks of transactions to be added to the blockchain.
- Every new block is either directly approved without any check or if all block generators vote unanimously or by a majority.
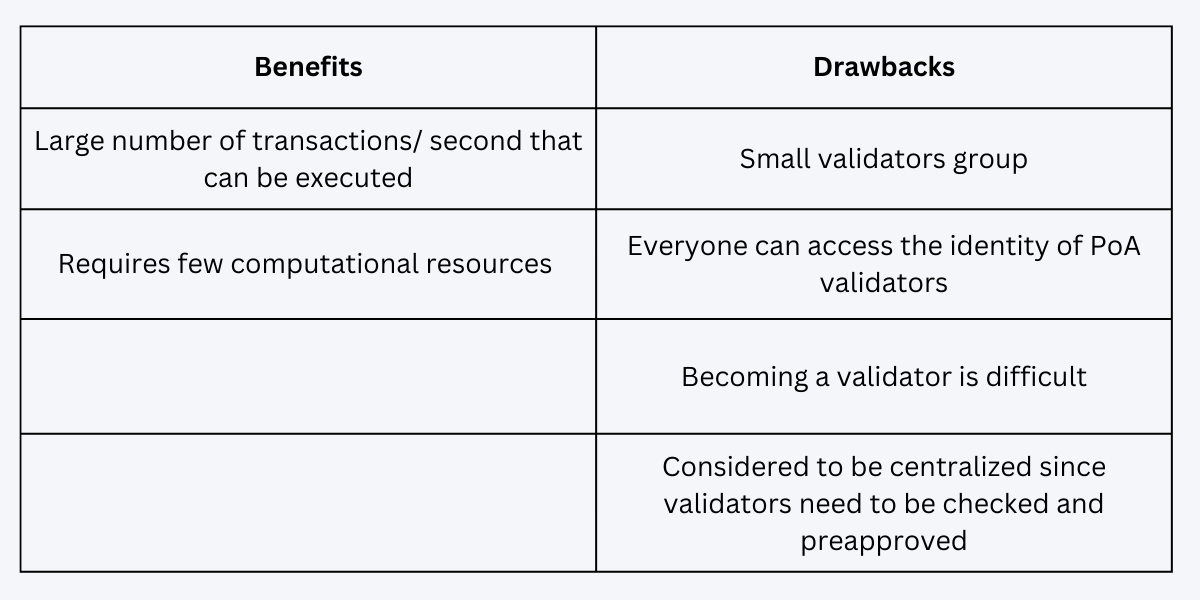
Benefits and Drawbacks
What is Zero Knowledge?
One party proves to another party that they know a piece of information without revealing what that information is. This would sum up what Zero Knowledge proof is all about. Basically, the only information that’s revealed is that a piece of hidden information is valid.
Zero Knowledge (ZK) is particularly useful for businesses that want to keep confidential databases private. That’s why typical use cases of ZK proof include financial and healthcare services, or any business service that requires identity verification.
For instance, IBM, Alibaba Group or Tencent Holding have integrated zero-knowledge proof to authenticate customer identity during customer onboarding, loan processing, or opening investment accounts.
How ZK Works
These rollups collect and process several batches of transactions (a process that is performed off-chain) and compress all this data into a single transaction. Then, they send it to Ethereum Mainnet as proof of their validity (a process that happens on-chain).
More details on how Zero Knowledge works.
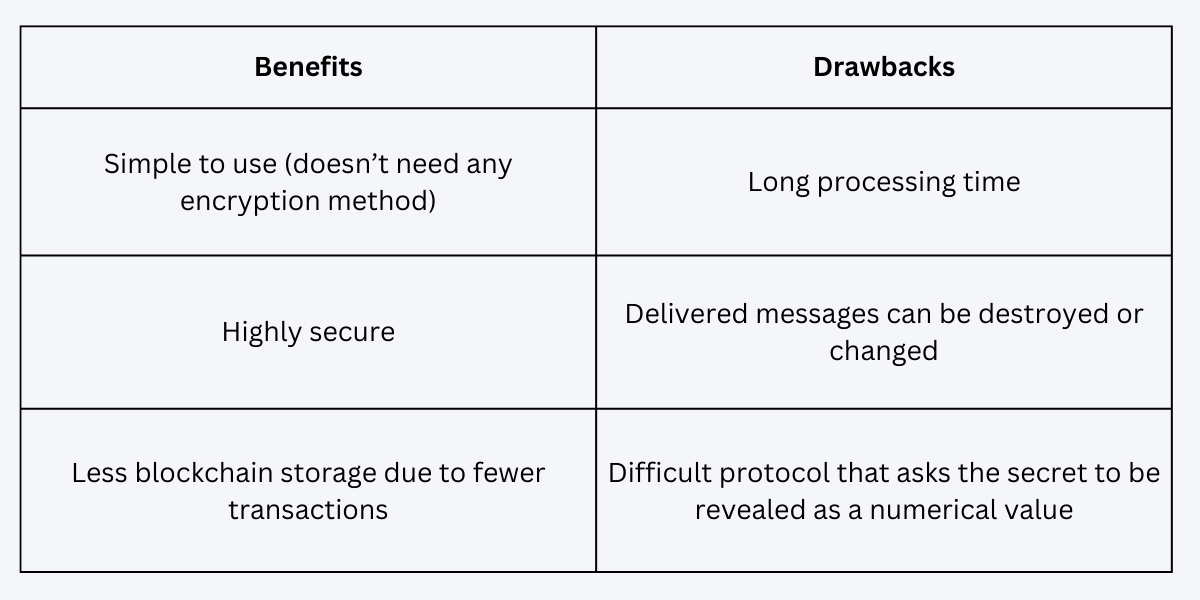
Benefits and Drawbacks
Summing Up
Now, let’s recap. Validation is easier with the PoA algorithm as it doesn’t require puzzle-solving to enable connection between nodes. But PoA works best in a centralized way, so it doesn’t facilitate decentralization as opposed to proof of stake.
Between the two of them, proof of authority is more secure. When it comes to the zero knowledge algorithm, it uses a high level of security and privacy as well, but so far, the process is a bit slower than most would expect.
The growth of Decentralized Applications (DApps), the security and scalability of cryptos, and several other possible use cases can all benefit from adopting the protocols or algorithms mentioned above, based on the most suitable use case.
Proof of stake seems to be the safest bet for cryptocurrencies, while proof of authority will likely enjoy adoption only by private companies due to the difficulties of becoming a validator.
On the other hand, Zero Knowledge proofs might become the next frontier for blockchain innovation, encompassing high privacy within Web3, Web2, and the physical world altogether.

